Using the Spark Job to Access DLI Metadata¶
Scenario¶
DLI allows you to develop a program to create Spark jobs for operations related to databases, DLI or OBS tables, and table data. This example demonstrates how to develop a job by writing a Java program, and use a Spark job to create a database and table and insert table data.
Constraints¶
You must create a queue to use Spark 3.1 for metadata access.
The following cases are not supported:
If you create a database with a SQL job, you cannot write a program to create tables in that database.
For example, the testdb database is created using the SQL editor of DLI. A program package for creating the testTable table in the testdb database does not work after it is submitted to a Spark Jar job.
The following cases are supported:
You can create databases and tables in a SQL job, and read and insert data using SQL statements or a Spark program.
You can create databases and tables in a Spark job, and read and insert data using SQL statements or a Spark program.
Environment Preparations¶
Before developing a Spark job to access DLI metadata, set up a development environment that meets the following requirements.
Item | Description |
|---|---|
OS | Windows 7 or later |
JDK | JDK 1.8. |
IntelliJ IDEA | This tool is used for application development. The version of the tool must be 2019.1 or other compatible versions. |
Maven | Basic configurations of the development environment. Maven is used for project management throughout the lifecycle of software development. |
Development Process¶
The following figure shows the process for developing a Spark job to access DLI metadata.
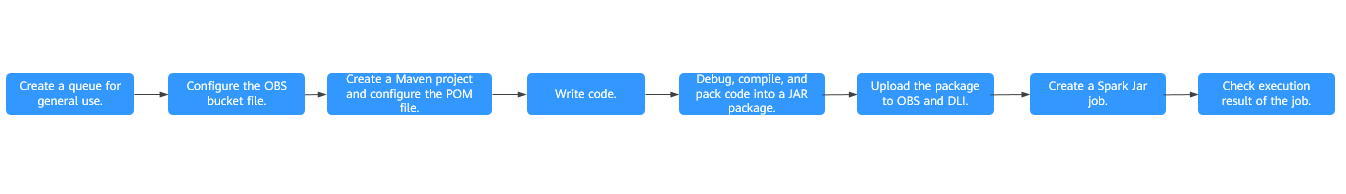
Figure 1 Development process¶
No. | Phase | Software Portal | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Create a queue for general use. | DLI console | The DLI queue is created for running your job. |
2 | Configure the OBS file. | OBS console |
|
3 | Create a Maven project and configure the POM file. | IntelliJ IDEA | Write a program to create a DLI or OBS table by referring to the sample code. |
4 | Write code. | ||
5 | Debug, compile, and pack the code into a Jar package. | ||
6 | Upload the Jar package to OBS and DLI. | OBS console | You can upload the generated Spark Jar package to an OBS directory and DLI program package. |
7 | Create a Spark JAR job. | DLI console | The Spark Jar job is created and submitted on the DLI console. |
8 | Check execution result of the job. | DLI console | You can view the job running status and run logs. |
Step 1: Create a Queue for General Purpose¶
If you submit a Spark job for the first time, you need to create a queue first. For example, create a queue, name it sparktest, and set Queue Usage to For general purpose.
In the navigation pane of the DLI management console, choose Queue Management.
In the upper right corner of the Queue Management page, click Create Queue to create a queue.
Create a queue, name it sparktest, and set the queue usage to for general purpose. For details about how to create a queue, see Creating a Queue.
Click Create Now to create a queue.
Step 2: Configure the OBS Bucket File¶
To create an OBS table, upload data to the OBS bucket directory.
Use the following sample data to create the testdata.csv file and upload it to an OBS bucket.
12,Michael 27,Andy 30,Justin
Log in to the OBS Console. In the Bucket page, click the name of the created OBS bucket. In this example, the bucket name is dli-test-obs01. The overview page is displayed.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Objects. Click Upload Object to upload the testdata.csv file to the root directory of the OBS bucket.
In the root directory of the OBS bucket, click Create Folder to create a folder and name it warehousepath. This folder is used to store DLI metadata in spark.sql.warehouse.dir.
Step 3: Create a Maven Project and Configure the POM Dependency¶
This step uses IntelliJ IDEA 2020.2 as an example.
Start IntelliJ IDEA and choose File > New > Project.
Figure 2 Creating a project¶
Choose Maven, set Project SDK to 1.8, and click Next.
Figure 3 Selecting an SDK¶
Set the project name, configure the storage path, and click Finish.
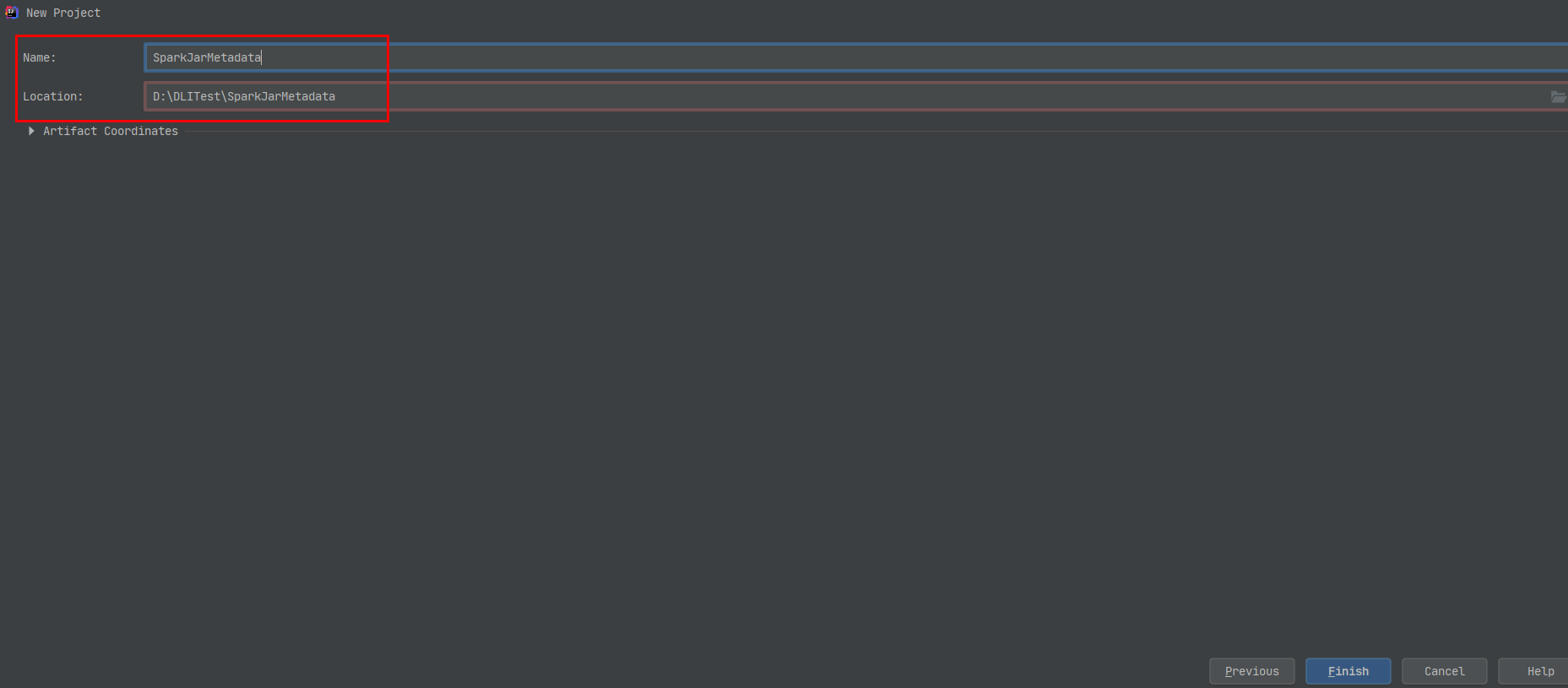
Figure 4 Creating a project¶
In this example, the Maven project name is SparkJarMetadata, and the project storage path is D:\DLITest\SparkJarMetadata.
Add the following content to the pom.xml file.
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId> <artifactId>spark-sql_2.11</artifactId> <version>2.3.2</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
Figure 5 Modifying the pom.xml file¶
Choose src > main and right-click the java folder. Choose New > Package to create a package and a class file.
Figure 6 Creating a package¶
Set the package name as you need. In this example, set Package to com.dli.demo and press Enter.
Create a Java Class file in the package path. In this example, the Java Class file is DliCatalogTest.
Step 4: Write Code¶
Write the DliCatalogTest program to create a database, DLI table, and OBS table.
For the sample code, see Java Example Code.
Import the dependency.
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession;
Create a SparkSession instance.
When you create a SparkSession, you need to specify spark.sql.session.state.builder, spark.sql.catalog.class, and spark.sql.extensions parameters as configured in the following example.
Spark 2.x and 3.1.x
SparkSession spark = SparkSession .builder() .config("spark.sql.session.state.builder", "org.apache.spark.sql.hive.UQueryHiveACLSessionStateBuilder") .config("spark.sql.catalog.class", "org.apache.spark.sql.hive.UQueryHiveACLExternalCatalog") .config("spark.sql.extensions","org.apache.spark.sql.DliSparkExtension") .appName("java_spark_demo") .getOrCreate();
Spark 3.3.x
SparkSession spark = SparkSession .builder() .config("spark.sql.session.state.builder", "org.apache.spark.sql.hive.DliLakeHouseBuilder") .config("spark.sql.catalog.class", "org.apache.spark.sql.hive.DliLakeHouseCatalog") .appName("java_spark_demo") .getOrCreate();
Create a database.
The following sample code shows how to create a database and named test_sparkapp.
spark.sql("create database if not exists test_sparkapp").collect();
Create a DLI table and insert test data.
spark.sql("drop table if exists test_sparkapp.dli_testtable").collect(); spark.sql("create table test_sparkapp.dli_testtable(id INT, name STRING)").collect(); spark.sql("insert into test_sparkapp.dli_testtable VALUES (123,'jason')").collect(); spark.sql("insert into test_sparkapp.dli_testtable VALUES (456,'merry')").collect();
Create an OBS Table. Replace the OBS path in the following example with the path you set in Step 2: Configure the OBS Bucket File.
spark.sql("drop table if exists test_sparkapp.dli_testobstable").collect(); spark.sql("create table test_sparkapp.dli_testobstable(age INT, name STRING) using csv options (path 'obs://dli-test-obs01/testdata.csv')").collect();
Disable the spark session.
spark.stop();
Step 5: Debug, Compile, and Pack the Code into a Jar Package.¶
Double-click Maven in the tool bar on the right, and double-click clean and compile to compile the code.
After the compilation is successful, double-click package.
The generated JAR package is stored in the target directory. In this example, SparkJarMetadata-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar is stored in D:\DLITest\SparkJarMetadata\target.
Step 6: Upload the JAR Package to OBS and DLI¶
Log in to the OBS console and upload the SparkJarMetadata-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar file to the OBS path.
Upload the file to DLI for package management.
Log in to the DLI management console and choose Data Management > Package Management.
On the Package Management page, click Create in the upper right corner.
In the Create Package dialog, set the following parameters:
Type: Select JAR.
OBS Path: Specify the OBS path for storing the package.
Set Group and Group Name as required for package identification and management.
Click OK.
Step 7: Create a Spark Jar Job¶
Log in to the DLI console. In the navigation pane, choose Job Management > Spark Jobs.
On the Spark Jobs page, click Create Job.
On the displayed page, configure the following parameters:
Table 3 Spark Jar job parameters¶ Parameter
Value
Queue
Select the DLI queue created for general purpose. For example, select the queue sparktest created in Step 1: Create a Queue for General Purpose.
Spark Version
Select a Spark version. Select a supported Spark version from the drop-down list. The latest version is recommended.
Job Name (--name)
Name of a custom Spark Jar job. For example, SparkTestMeta.
Application
Select the package uploaded to DLI in Step 6: Upload the JAR Package to OBS and DLI. For example, select SparkJarObs-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar.
Main Class (--class)
The format is program package name + class name.
Spark Arguments (--conf)
spark.dli.metaAccess.enable=true
spark.sql.warehouse.dir=obs://dli-test-obs01/warehousepath
Note
Set spark.sql.warehouse.dir to the OBS path that is specified in Step 2: Configure the OBS Bucket File.
Access Metadata
Select Yes.
Retain default values for other parameters.
Click Execute to submit the Spark Jar job. On the Job management page, view the running status.
Step 8: View Job Execution Result¶
On the Job management page, view the running status. The initial status is Starting.
If the job is successfully executed, the job status is Finished. Perform the following operations to view the created database and table:
On the DLI console, choose SQL Editor in the left navigation pane. The created database test_sparkapp is displayed in the database list.
Double-click the database name to view the created DLI and OBS tables in the database.
Double-click dli_testtable and click Execute to query data in the table.
Comment out the statement for querying the DLI table, double-click the OBS table dli_testobstable, and click Execute to query the OBS table data.
If the job fails, the job status is Failed. Click More in the Operation column and select Driver Logs to view the running log.
After the fault is rectified, click Edit in the Operation column of the job, modify job parameters, and click Execute to run the job again.
Follow-up Guide¶
For details about the syntax for creating DLI tables, see "SQL Syntax of Batch Jobs" > "Creating a DLI Table" in Data Lake Insight SQL Syntax Reference. For details about the syntax for creating OBS tables, see "SQL Syntax of Batch Jobs" > "Creating an OBS Table" in Data Lake Insight SQL Syntax Reference.
If you submit the job by calling an API, perform the following operations:
Call the API for creating a batch processing job. The following table describes the request parameters.
Set catalog_name in the request to dli.
Add "spark.dli.metaAccess.enable":"true" to the CONF file.
Configure "spark.sql.warehouse.dir": "obs://bucket/warehousepath" in the CONF file if you need to run the DDL.
The following example provided you with the complete API request.
{ "queue":"citest", "file":"SparkJarMetadata-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar", "className":"DliCatalogTest", "conf":{"spark.sql.warehouse.dir": "obs://bucket/warehousepath", "spark.dli.metaAccess.enable":"true"}, "sc_type":"A", "executorCores":1, "numExecutors":6, "executorMemory":"4G", "driverCores":2, "driverMemory":"7G", "catalog_name": "dli" }
Java Example Code¶
This example uses Java for coding. The complete sample code is as follows:
package com.dli.demo;
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession;
public class DliCatalogTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparkSession spark = SparkSession
.builder()
.config("spark.sql.session.state.builder", "org.apache.spark.sql.hive.UQueryHiveACLSessionStateBuilder")
.config("spark.sql.catalog.class", "org.apache.spark.sql.hive.UQueryHiveACLExternalCatalog")
.config("spark.sql.extensions","org.apache.spark.sql.DliSparkExtension")
.appName("java_spark_demo")
.getOrCreate();
spark.sql("create database if not exists test_sparkapp").collect();
spark.sql("drop table if exists test_sparkapp.dli_testtable").collect();
spark.sql("create table test_sparkapp.dli_testtable(id INT, name STRING)").collect();
spark.sql("insert into test_sparkapp.dli_testtable VALUES (123,'jason')").collect();
spark.sql("insert into test_sparkapp.dli_testtable VALUES (456,'merry')").collect();
spark.sql("drop table if exists test_sparkapp.dli_testobstable").collect();
spark.sql("create table test_sparkapp.dli_testobstable(age INT, name STRING) using csv options (path 'obs://dli-test-obs01/testdata.csv')").collect();
spark.stop();
}
}
Scala Example Code¶
object DliCatalogTest {
def main(args:Array[String]): Unit = {
val sql = args(0)
val runDdl =
Try(args(1).toBoolean).getOrElse(true)
System.out.println(s"sql is $sql
runDdl is $runDdl")
val sparkConf = new SparkConf(true)
sparkConf
.set("spark.sql.session.state.builder","org.apache.spark.sql.hive.UQueryHiveACLSessionStateBuilder")
.set("spark.sql.catalog.class","org.apache.spark.sql.hive.UQueryHiveACLExternalCatalog")
sparkConf.setAppName("dlicatalogtester")
val spark = SparkSession.builder
.config(sparkConf)
.enableHiveSupport()
.config("spark.sql.extensions","org.apache.spark.sql.DliSparkExtension")
.appName("SparkTest")
.getOrCreate()
System.out.println("catalog is "
+ spark.sessionState.catalog.toString)
if (runDdl) {
val df = spark.sql(sql).collect()
} else {
spark.sql(sql).show()
}
spark.close()
}
}
Example Python Code¶
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
from __future__ import print_function
import sys
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
if __name__ == "__main__":
url = sys.argv[1]
creatTbl = "CREATE TABLE test_sparkapp.dli_rds USING JDBC OPTIONS ('url'='jdbc:mysql://%s'," \
"'driver'='com.mysql.jdbc.Driver','dbtable'='test.test'," \
" 'passwdauth' = 'DatasourceRDSTest_pwd','encryption' = 'true')" % url
spark = SparkSession \
.builder \
.enableHiveSupport() \
.config("spark.sql.session.state.builder","org.apache.spark.sql.hive.UQueryHiveACLSessionStateBuilder") \
.config("spark.sql.catalog.class", "org.apache.spark.sql.hive.UQueryHiveACLExternalCatalog") \
.config("spark.sql.extensions","org.apache.spark.sql.DliSparkExtension") \
.appName("python Spark test catalog") \
.getOrCreate()
spark.sql("CREATE database if not exists test_sparkapp").collect()
spark.sql("drop table if exists test_sparkapp.dli_rds").collect()
spark.sql(creatTbl).collect()
spark.sql("select * from test_sparkapp.dli_rds").show()
spark.sql("insert into table test_sparkapp.dli_rds select 12,'aaa'").collect()
spark.sql("select * from test_sparkapp.dli_rds").show()
spark.sql("insert overwrite table test_sparkapp.dli_rds select 1111,'asasasa'").collect()
spark.sql("select * from test_sparkapp.dli_rds").show()
spark.sql("drop table test_sparkapp.dli_rds").collect()
spark.stop()